Swedish Export Credit System
To facilitate and promote exports and the internationalisation and competitiveness of Swedish industry, Sweden offers a government backed export credit system. The combined offer facilitates the financing of transactions with Swedish exporting companies and has strong benefits for all parties involved.

How to finance a Swedish export contract
Export transactions often involve large contracts and buyers that require long repayment periods. A common form of financing is an export credit provided by a commercial bank – a buyer’s credit.
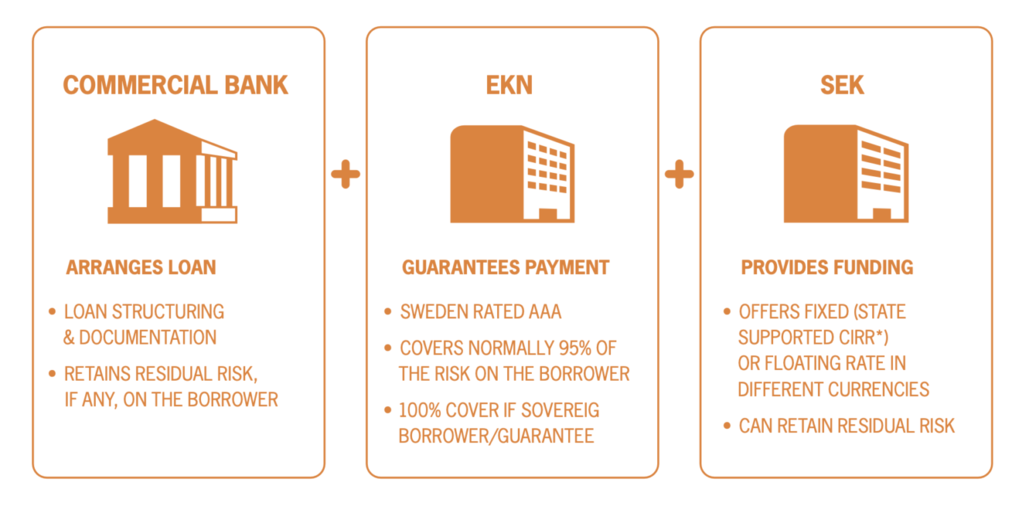
Financing of a large Swedish export contract usually involves a commercial bank as the arranger. The bank, or a group of banks, arranges and administers a loan to the buyer in the export contract. EKN is the guarantor, taking the repayment risk with a small portion of the risk retained by the arranging bank.
- When the borrower is a sovereign the cover is 100%. SEK can provide funding, and also sometimes assume the role as arranger, usually jointly with one or more banks.
See an example below.
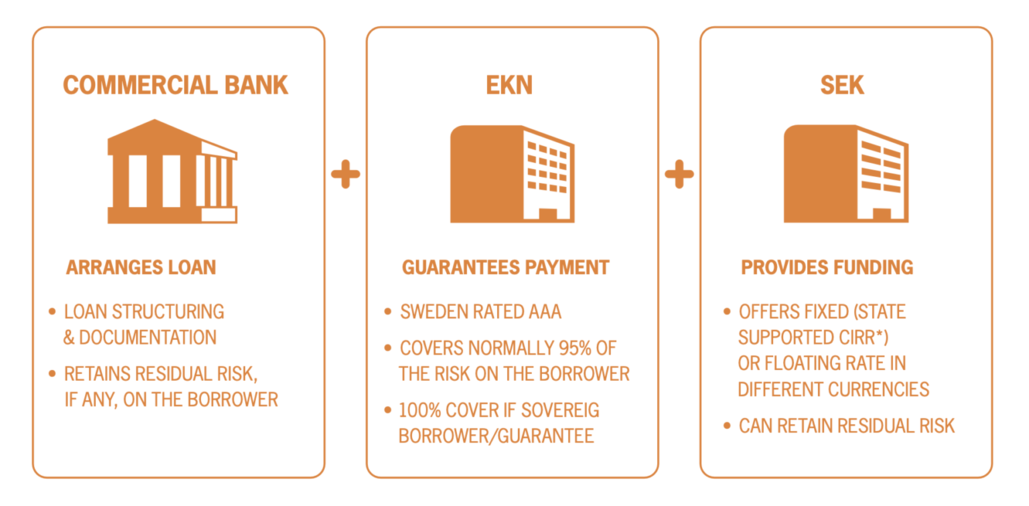
*The Commercial Interest Reference Rate, CIRR, is a state-supported interest rate administered by SEK. It allows exporting companies to offer their customers funding at a favourable fixed interest rate.

How it works
To ensure the best conditions for all parties involved it is very important for the exporter and bank to contact EKN and SEK at an early stage. This is to enable structuring of the business agreements regarding securities, capital structure, and being OECD-compliant. In their environmental and social due diligence, EKN and SEK comply with international standards.
Below is a schematic outline for a buyer’s credit. Please note that the steps can take place simultaneously.
-
The exporting company and the buyer sign a sales contract. Payment is to be made at delivery, or with a short credit period.
-
A bank signs a loan agreement with the buyer.
-
The bank applies for a guarantee – preferably before the contract is signed, and receives an offer from EKN. EKN normally covers 95 % of the loan. The bank notifies EKN of disbursements and receives the guarantee. This is when the premium is paid.
-
If the bank is looking for funding they will have contacted SEK and received an offer, before signing the contract. The bank will then assign the loan as well as the rights under the EKN guarantee to SEK.
The bank retains the 5 % risk share on the borrower as well as their obligations to EKN, and administers the loan. If the borrower fails to pay according to the loan agreement, EKN will indemnify SEK directly.